
Curetonit in Matrix
Redhouse Barite Mine, Osgood Mountains, Golconda, Nevada, USA (TL)
Stufe: 3,8 x 2,0 cm
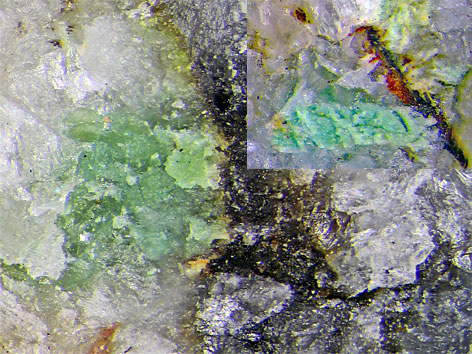
Curetonit-Einschlüsse in Matrix
Detail der links abgebildeten Stufe
Größe der Einschlüsse: ca. 2 mm
|
Curetonit |
|
|
Formel: |
Ba(Al,Ti4+)(PO4)(O,OH)F (8.BK.15; Curetonit-Gruppe) |
|
Ausbildung: |
monoklines Kristallsystem; gelblichgrün, keilförmige Kristalle bis 3 mm Größe und als kristalline Einschlüsse |
|
Entdeckung: |
IMA 1978-065; 1979 - Williams; benannt zu Ehren von Forrest Ellsworth Cureton II (1932 - 2020), ein Mineralienhändler, welcher mit seinem Sohn Michael Edward Cureton (1960 - ...), das Mineral entdeckte |
|
Typlokalität: |
USA, Nevada, Humboldt Co., Golconda, Osgood Mountains, Potosi Mining District, Redhouse Barite Mine |
|
Seltenheit: |
höchst selten (Mineralienatlas: 1 / Mindat: 1 Lokalitäten; 2023) |
 Curetonit in Matrix Redhouse Barite Mine, Osgood Mountains, Golconda, Nevada, USA (TL) Stufe: 3,8 x 2,0 cm
|
 Curetonit-Einschlüsse in Matrix Detail der links abgebildeten Stufe Größe der Einschlüsse: ca. 2 mm
|
Quellen: Sammlung und Fotos Matthias Kahl; allg. Mineralbeschreibung nach Mineralienatlas.de, Mindat.org, Handbook of Mineralogy, DeWikipedia und/oder Lapis-Mineralienmagazin
© copyright Matthias Kahl